OtolaryngologyHead and Neck Surgery 2000 122. Ad Life Is Good.
 Asymmetrical Sensorineural Hearing Loss Fitting Strategies Donald J Schum Hearing Aids Adults 12222
Asymmetrical Sensorineural Hearing Loss Fitting Strategies Donald J Schum Hearing Aids Adults 12222
Vestibular schwannoma a benign tumor that presses on the inner ear nerves.
Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss. Comment on Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click on download. Your GP found nothing untoward and so referred you to our audiology team to see if a hearing aid would benefit you.
The presentation of unilateral or asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss ASNHL raises the possibility of vestibular schwannoma VS. Prolonged uneven exposure to noise. Defining significant asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss ASNHL is important to determine if a patient requires further evaluation for retrocochlear pathology.
Vestibular schwannomas usually present with unilateral or asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss tinnitus and dizziness or imbalance. No matter the degree of loss asymmetric hearing loss requires further evaluation. In children the most common causes of SNHL include inner ear abnormalities genetic variations jaundice or a yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes and viral infection from the mother during pregnancy.
Sensorineural hearing loss diagnosis Doctors use. Although ASNHL is common in clinical practice VS is rare and definitive diagnosis by imaging is costly. Generally this workup includes auditory brainstem response ABR testing or MRI.
Currently gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging MRI is the gold standard to identify pathology in the internal auditory canal IAC and cerebellopontine angle CPA responsible for ASNHL. Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss. Prior studies indicate only 2 to 8 of patients with an asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss have a vestibular schwannoma.
Asymmetric hearing loss usually occurs for one of the following reasons. Routinely patients presenting with ASSNHL undergo a battery of serologic testing and imaging in an attempt to determine a cause. Asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss occurs in about 35 to 50 of the population depending on how strictly asymmetric is defined.
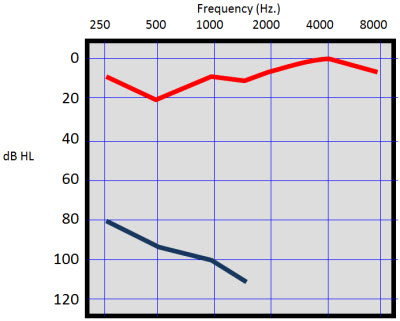
A number of factors have been identified that contribute to the presentation of asymmetric sudden sensorineural hearing loss ASSNHL. Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss ASNHL is defined as binaural difference in bone conduction thresholds of 10 dB at two consecutive frequencies or 15 dB at one frequency 02580 kHz 3. Asymmetrical sensorineural hearing loss Your journey so far Most likely you have noticed a gradual decline in your hearing.
Ad Life Is Good. Asymmetric hearing loss has been defined as a difference of 15 dB between the right and left ears at three contiguous frequencies. We Improve Your Hearing To Enhance Your Everyday.
Asymmetrical SNHL occurs when theres hearing loss on both sides but one side is worse than the other. The objective of this study was to assess the utility of this diagnostic. Patients in whom these symptoms are asymmetric or unilateral should be referred to an otolaryngologist.
Today an audiologist has examined your ears asked you about your hearing and performed a hearing test. Asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss. 10793373 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types.
Sensorineural hearing loss SNHL happens when there is damage to tiny hair cells in the cochlear andor the auditory nerve. If you have the appropriate software installed you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss.
Viral infections of the hearing nerves. A simple and reliable set of criteria to select patients for further evaluation would be very helpful but. 5 780-780 Download Citation.
Hearing Loss Sensorineuraldiagnosis Hearing Loss Sensorineuraletiology. We Improve Your Hearing To Enhance Your Everyday.
