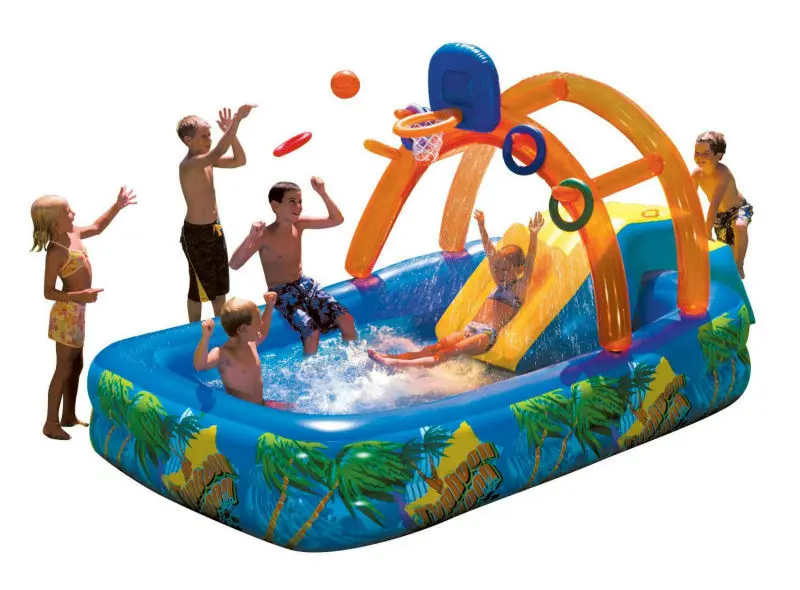
A mental health evaluation is needed to diagnose OCD. Aggressive thoughts about self-harm and harm to others Thoughts about doing offensive sexual acts or taboo behaviors.
Obsessions are repeated bothersome thoughts that are different from the worries most of us experience occasionally.

Ocd symptoms in kids. Obsessions may include extreme fears or disturbing frightening thoughts related to the baby and her health while compulsions are repeated behaviors that. Read about obsessions and compulsions Examples of obsessive thoughts in. Disturbing and unwanted thoughts or images of violent or disturbing things like harming others Extreme worry about bad things happening or doing something wrong or lying.
Cleaning rituals related to the house or other items. OCD may be related to mental health disorders such as body dysmorphic disorders hoarding disorders skin picking trichotillomania and tic disorders in some children. OCD in kids is usually diagnosed between the ages of 7 and 12.
Children with OCD dont have enough of a chemical called serotonin in their brain. These obsessions are unpleasant for the child and typically cause a lot of worry anxiety and distress. OCD is a condition where children have obsessions which are unwanted intrusive thoughts that children find distressing and difficult to fight.
Obsessions are intrusive and unwanted thoughts images or urges that occur over and over again and feel outside of the childs control. The behaviors are called compulsions. Flatten out sheets check for bugs.
You may notice signs of. The thoughts are called obsessions. They pop up again and again even when the person does not want to be thinking about them.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder OCD which causes intense recurring unwanted thoughts obsessions or rituals compulsions Panic Disorders which cause unexpected and repeated episodes of intense fear accompanied by physical symptoms such as chest pain heart palpitations shortness of breath dizziness or abdominal distress. These are called obsessions and they can make kids feel anxious. OCD symptoms in children also fluctuate in content and intensity based on schedule changes nutrition exercise frequency sickness sleep quality and quantity and solitude in the home and school life.
Most children may not show any apparent signs and symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder since it has a gradual onset. Obsessive-compulsive disorder OCD is a condition that causes kids to have unwanted thoughts feelings and fears. Teach Kids to Fight OCD by Bullying it Back Example of Possible Early Signs.
The symptoms of OCD in children involve repetitive thoughts or images called obsessions. To relieve the obsessions and anxiety OCD leads kids to do behaviors called compulsions also called rituals. These obsessions cause the child to experience increased anxiety leading the child to engage in a compulsion which is a behavior that then neutralizes the thought and reduces the anxiety.
Common OCD Symptoms in Children OCD has two main symptoms. Symptoms And Signs Of OCD In Children. Common obsessions among children with OCD include.
Children may have an obsessive-compulsive disorder OCD when unwanted thoughts and the behaviors they feel they must do because of the thoughts happen frequently take up a lot of time more than an hour a day interfere with their activities or make them very upset. Compulsions represent the ritual behaviors that they repeat again and again to banish the thoughts. Compulsive behaviors include hoarding objects and checking things often.
Symptoms of OCD in children can be different from those in adults based on how they appear in the classroom and at home. Ask the Child Therapist Episode 102 Kids Edition. Having to do the same exact behavior when tucking your child into bed eg.
A child with OCD will experience symptoms of obsession and compulsion. Symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder in children change over time seasonally at certain developmental milestones and with hormonal changes. The signs and symptoms of OCD in children can be categorized by obsessions and compulsions.
How OCD Manifests in Children OCD is said to be childhood-onset if symptoms such as obsessions and compulsions occur before puberty. Between 1 and 3 of children will develop OCD and the average age of onset is approximately 10 years of age although children as young as 5 or 6 may develop the illness. Since these are the years when kids naturally feel concerned about fitting in with their friends the discomfort and stress brought on by OCD can make them feel scared out of control and alone.
Obsessive symptoms include repeated doubts and extreme preoccupation with dirt or germs. Obsessive compulsive disorder OCD is characterized by both obsessions and compulsions. Symptoms vary from child to child however t he most common obsessions children experience include.
Postpartum obsessive-compulsive disorder can include many of the same symptoms of postpartum anxiety such as extreme worry but OCD symptoms take the form of obsessions andor compulsions.