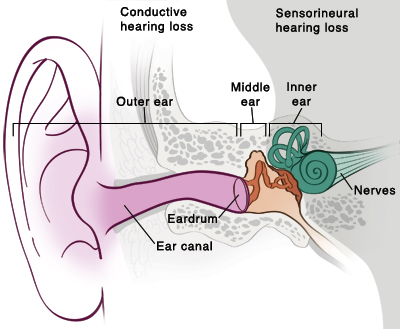
For example SIDS is more likely to affect a baby who is between 1 and 4 months old it is more common in boys than girls and most deaths occur during the fall winter and early spring months. Factors that may place a baby at higher risk of dying from SIDS include the following.
 Sids Risk Factors By Age Group A Download Table
Sids Risk Factors By Age Group A Download Table
SIDS risk also decreases after 6.

When is sids risk over. But specific risk factors do exist. There are no symptoms or warning signs that point to the likelihood of suffering from SIDS. Rather several risk factors might exist together to cause an infant to.
The SIDS risk significantly decreases after your baby turns 6 months old and is rolling over which is a sign she is developing head and neck control. Unknown cause infant mortality rates remained unchanged from 1990 until 1998 when rates began to increase. Infants younger than six months old represent roughly 90 percent of all SIDS-related deaths.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome SIDS sometimes known as crib death is a condition that babies less than a year old may develop that can rapidly lead to infant mortality. Babies between 1 and 4 months old are most at risk for sudden infant death syndrome SIDS and 90 percent of cases occur in babies under the age of 6 months. Heres what you need to know about SIDS and what you can do to prevent it.
In 2018 the unknown cause mortality rate in infants was 337 deaths per 100000 live births. Sometimes other terms such as SUDI SUDC or unascertained may be used. Additionally preterm infants with low birth weights are considered at higher risk of SIDS.
Some babies are more at risk than others. The classic definition of sids involves all unexplained deaths under a year which enables researchers a zone to focus on. SIDS rates declined considerably from 1303 deaths per 100000 live births in 1990 to 352 deaths per 100000 live births in 2018.
SIDS also tends to be slightly more common in baby boys. Risk less by 4mo. About 2300 babies in the United States die of SIDS each year.
The peak SIDS age is typically 1 to 4 months with the vast majority of cases occurring before 6 months. Its believed the risk of SIDS peaks between one and four months. Most deaths happen during the first 6 months of a babys life.
When a baby who usually sleeps on their back is suddenly laid on their stomach to sleep the risk of SIDS is much higher. Deaths that remain unexplained after the post-mortem are usually registered as sudden infant death syndrome SIDS or sudden unexplained death in childhood SUDC in a child over 12 months. Consistent back sleeping is considered especially important for preterm infants.
If youre worried your baby might choke while sleeping on. No single factor is likely to cause death from SIDS. By definition SIDS doesnt happen after a childs first birthday.
Infants born prematurely or with a low birthweight are at greater risk. The adult smokes has recently had alcohol or is tired. Babies who usually sleep on their backs but who are then placed to sleep on their stomachs such as for a nap are at very high risk for SIDS.
However there is a significant fall off in the frequency after a child reaches 4mo for reasons that are unclear. Research shows that several factors put babies at higher risk for SIDS and other sleep-related causes of infant death. Most SIDS deaths occur in the first several months of a babys life and in fact infants are most vulnerable between the second and fourth months.
Although the causes of SIDS sudden infant death syndrome are still largely unknown doctors do know that the risk of SIDS appears to peak between 2 and 4 months. SIDS usually occurs when a baby is asleep although it can occasionally happen while theyre awake. And the risk of SIDS is up to 19 times higher for babies when they are used to sleeping on their backs but wind up on their stomachs for some reason the researchers wrote in the paper.
In general younger babies are more susceptible to SIDS than older ones. SIDS is also more likely to strike in the winter. SIDS is mysterious since by definition its cause is undetermined.
Boys black infants and Native American babies tend to be at higher risk than girls or Caucasian infants.