Body will develop a milder immune response and recover. First the flu virus appears to survive better in cold dry weather with reduced ultraviolet light.
 Will Warmer Weather Stop The Spread Of Coronavirus
Will Warmer Weather Stop The Spread Of Coronavirus
It is still unclear if this coronavirus will be similarly impacted.

At what temperature does the flu virus die. The researchers from Yale infected airway cells with a rhinovirus in their lab and kept some at a normal body temperature 98 degrees Fahrenheit and others just below it 914 degrees. But when humidity levels were raised to. During this period if the body temperature is above 365C and better still above 37C the virus is attenuated or killed.
Scientists did a deep dive into the data and found that while low humidity and low temperatures mean more flu outbreaks whats considered a low. Strictly speaking viruses cant die for the simple reason that they arent alive in the first place. At humidity levels of 23 percent 70 to 77 percent of the flu virus particles were still able to cause an infection an hour after the coughing simulation.
According to the World Health organisation WHO cooking of poultry eg. At warmer temperatures however the gel melts to a liquid phase. Cooler temperatures apparently cause the virus.
The researchers found that the virus was killed after 5 minutes at 70C 158F. The answer to that is that is sadly yes. Do existing strains die off each spring only to be replaced each fall by new founding strains from other parts of the world or does a hidden chain of sickness persist over the summer seeding.
The researchers discovered that at temperatures slightly above freezing and below the viruss lipid covering solidified into a gel. At temperatures above 70 degrees Fahrenheit the lipids gel begins to melt transforming into a liquid according to the NIH study. Chicken ducks and geese at or above 70 degree Celsius so that absolutely no meat remains raw.
Instead they must invade a host organism and hijack its genetic instructions. Hot temperatures can kill most germs usually at least 140 degrees Fahrenheit. Freezing temperatures dont kill germs but it.
Whether its cold or hot infected cells tend to make little interferons Tech Times reported but in the two temperature groups the virus persisted. And of course it spread but by varying air temperature and humidity in the guinea pigs quarters the flu spread rapidly and very well when the temperature was set at 41 degrees Fahrenheit. Although they contain genetic instructions in the form of DNA or the related molecule RNA viruses cant thrive independently.
In fact the cells in below-average temps replicated. Meaning those viruses do tend to favor cold weather direr conditions and as things heat up and humidity goes up you tend to see those viruses receding According to the National Institute of Health cold temperatures essentially fortify the outer layer of the flu virus but high temperatures and humidity levels cause the virus to become weaker and not as infectious. One study in Applied Physics Letters used mathematical modeling to predict the effect of different temperatures on.
Most bacteria thrive at 40 to 140 degrees Fahrenheit which is why its important to keep food refrigerated or cook it at high temperatures. As temperatures approach 60 degrees Fahrenheit the covering gradually thaws eventually melting to a soupy mix. During the summer when the ambient temperature is much higher the hemagglutinin coat is not able to stay hard and protect the virus which is more likely to die before it can infect people.
At about 70 degrees Fahrenheit much of the lipid was still in gel form. Some viruses like those that cause the flu are seasonal meaning they spread more easily in warm dry air. Think about how a lot of times we use heat to kill things or.
That said it makes sense to talk of.
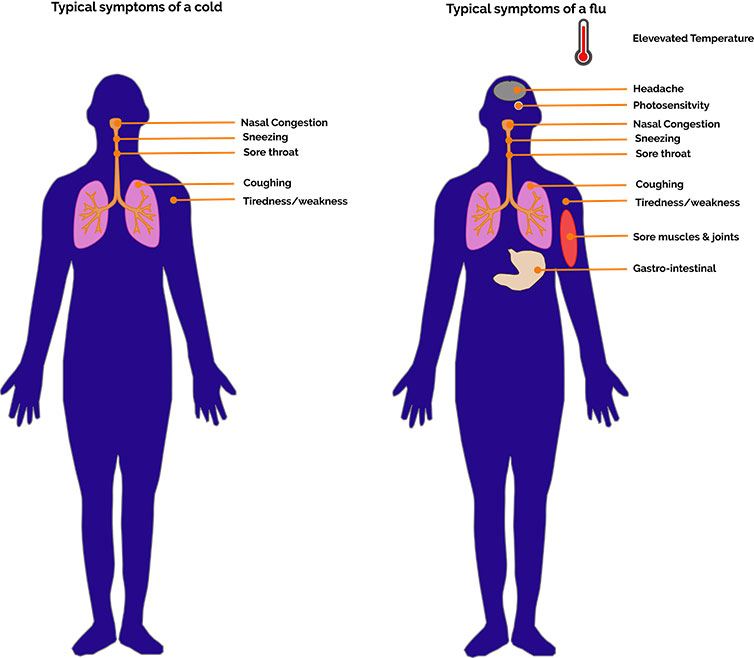 Understanding Cold And Flu Viruses Oxford Instruments
Understanding Cold And Flu Viruses Oxford Instruments
 Roles Of Humidity And Temperature In Shaping Influenza Seasonality Journal Of Virology
Roles Of Humidity And Temperature In Shaping Influenza Seasonality Journal Of Virology
 The Reason For The Season Why Flu Strikes In Winter Science In The News
The Reason For The Season Why Flu Strikes In Winter Science In The News
 Effects Of High Temperature On Pandemic And Seasonal Human Influenza Viral Replication And Infection Induced Damage In Primary Human Tracheal Epithelial Cell Cultures Sciencedirect
Effects Of High Temperature On Pandemic And Seasonal Human Influenza Viral Replication And Infection Induced Damage In Primary Human Tracheal Epithelial Cell Cultures Sciencedirect
 The Reason For The Season Why Flu Strikes In Winter Science In The News
The Reason For The Season Why Flu Strikes In Winter Science In The News
 The Human Antibody Response To Influenza A Virus Infection And Vaccination Nature Reviews Immunology
The Human Antibody Response To Influenza A Virus Infection And Vaccination Nature Reviews Immunology
 Scientists Ask Could Summer Heat Help Beat Covid 19 Coronavirus The Guardian
Scientists Ask Could Summer Heat Help Beat Covid 19 Coronavirus The Guardian
 Novel Coronavirus Summer Temperatures In India To Keep Virus At Bay
Novel Coronavirus Summer Temperatures In India To Keep Virus At Bay
 Temperature Dependent Growth Of Different Serotypes Of Influenza Download Scientific Diagram
Temperature Dependent Growth Of Different Serotypes Of Influenza Download Scientific Diagram
Cold Weather Really Does Spread Flu New Scientist
Avian Influenza Virus Glycoproteins Restrict Virus Replication And Spread Through Human Airway Epithelium At Temperatures Of The Proximal Airways



No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.