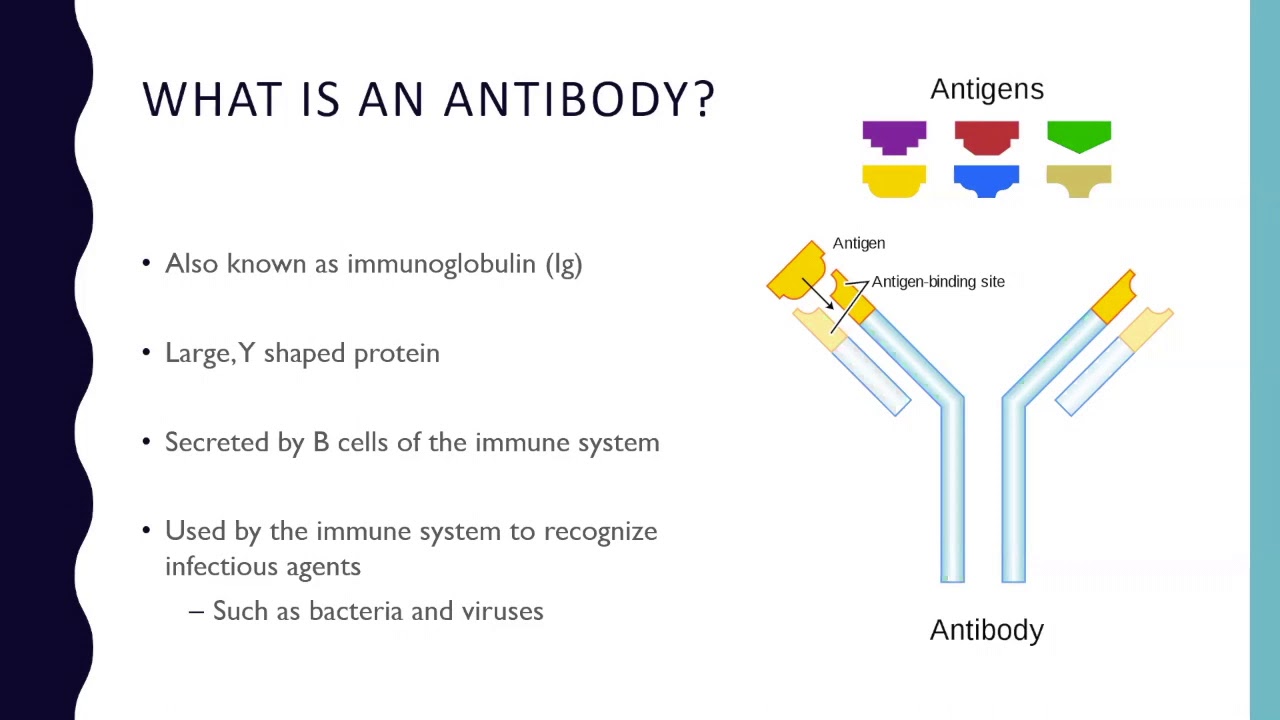
An antibody is a protein component of the immune system that circulates in the blood recognizes foreign substances like bacteria and viruses and neutralizes them. An antibody is a protein made by immune cells that is just the right shape and size to attach itself to a specific spot on a particular foreign substance such as a virus or bacteria in the blood.
 Antibodies 101 Every Body Needs An Anti Body
Antibodies 101 Every Body Needs An Anti Body
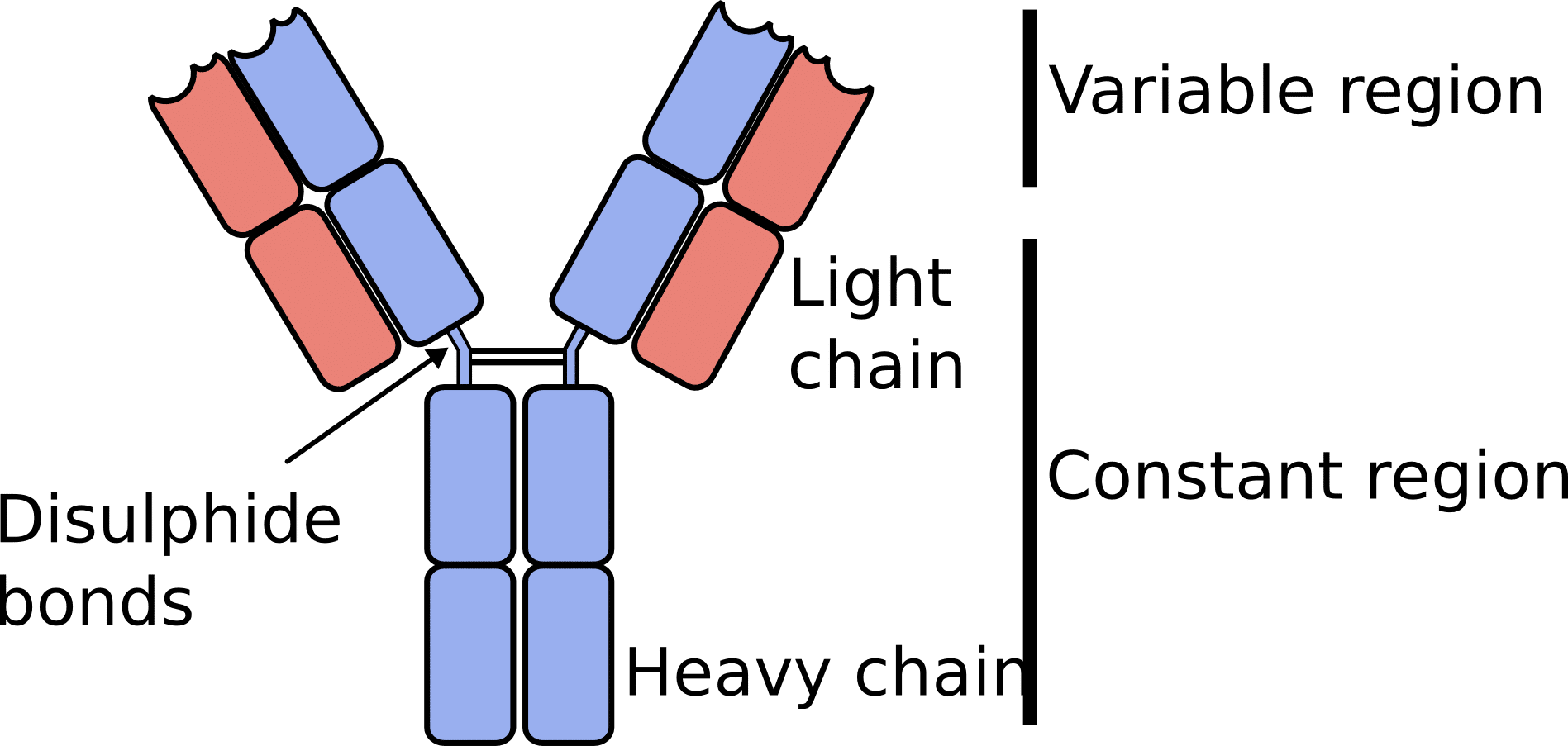
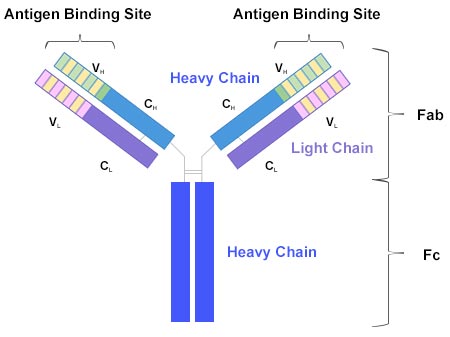
An antibody is a class of protein called an immunoglobulin which is made by specialised white blood cells to identify and neutralise material foreign to an immune system.

What is an anti body. Antibody antĭ-bode an immunoglobulin molecule having a specific amino acid sequence that gives each antibody the ability to adhere to and interact only with the antigen that induced its synthesis. What Is an Antibody Test. Your body makes these when it fights an infection like.
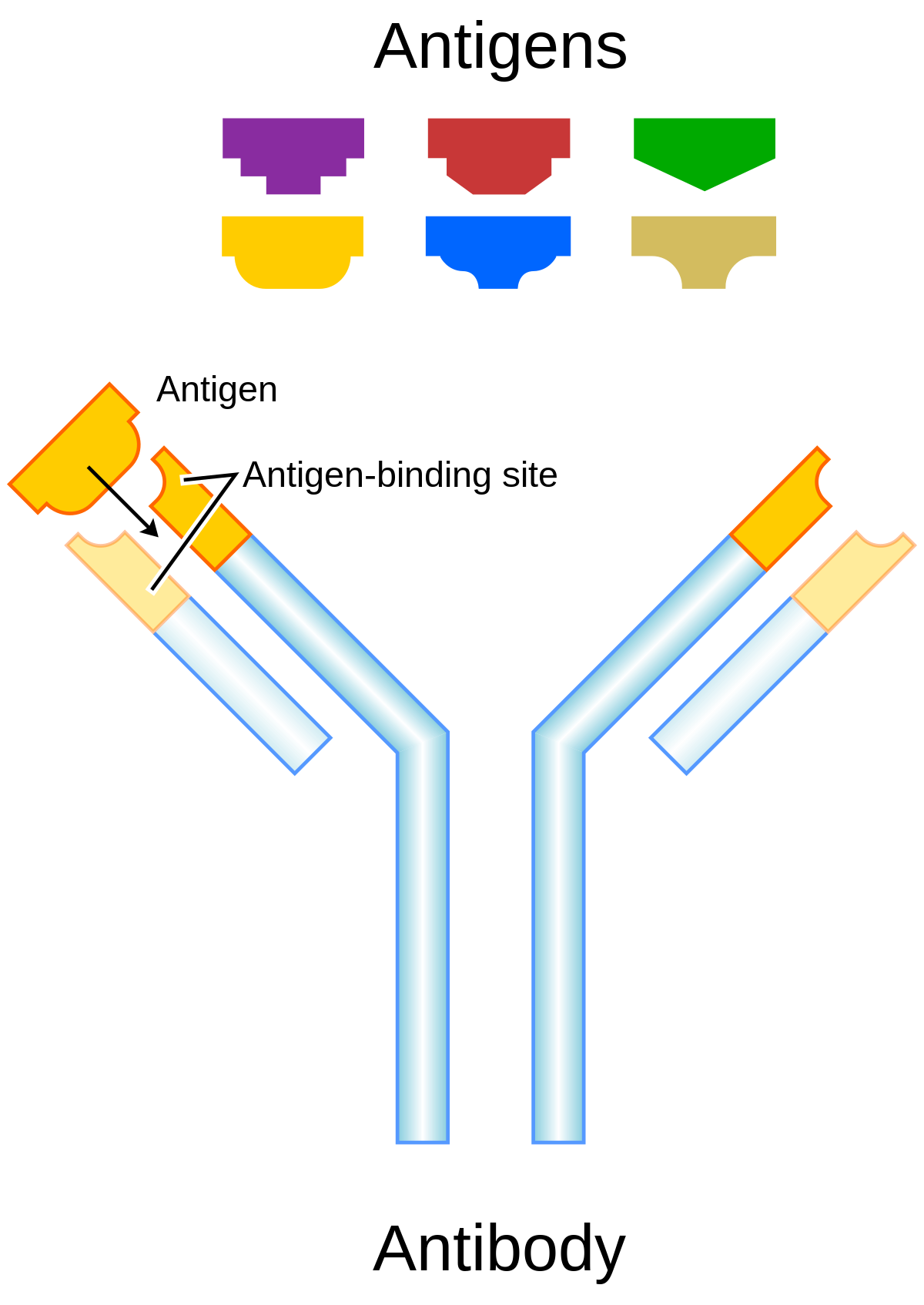
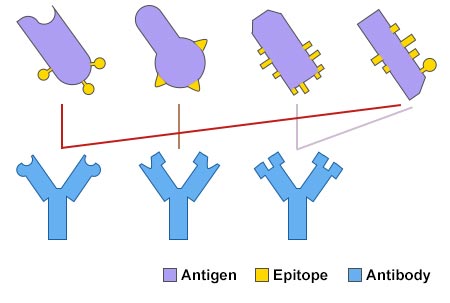
This antigen-specific property of the antibody is the basis of the antigen-antibody reaction that is essential to an immune response. The scientific term for such unfamiliar molecules is antigens. The definition of an antibody is a protein molecule that can be found in the blood and is intended to attack bacteria viruses and transplanted organs.
Learn more about the function and structure of antibodies in this article. Examples of antigens include microorganisms bacteria fungi parasites and viruses and chemicals. Antibodies are also called immunoglobulins or Ig.
An antibody is a protein produced by the immune system that is capable of binding with high specificity to an antigen. An example of an antibody is rituximab. An antibody is a protein produced by the bodys immune system when it detects harmful substances called antigens.
Antibodies are proteins created by the bodys immune system to fight a particular virus such as SARS-CoV-2. They are Y-shaped proteins made by your immune systems B lymphocytes or B cells. Antibody a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the presence of a foreign substance called an antigen.
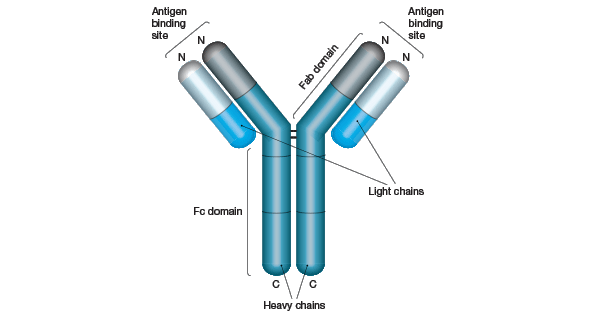
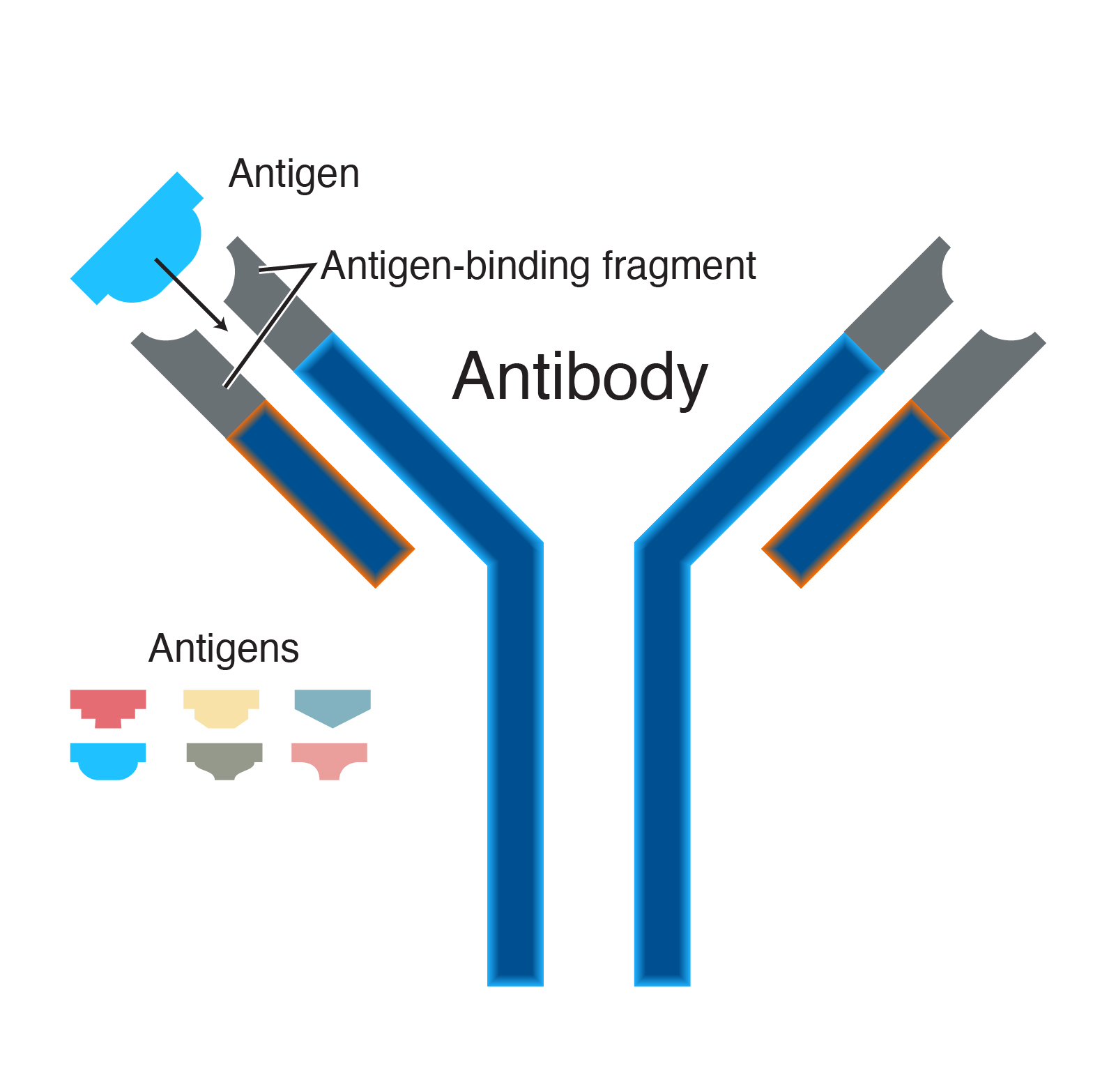
Antibodies are specialized Y-shaped proteins that bind like a lock-and-key to the bodys foreign invaders whether they are viruses bacteria fungi or. Antibodies recognize and latch onto antigens in order to remove them from the body. By attaching the antibody can potentially directly stop these invaders from causing an infection or it can mark them for destruction by immune cells.
The bodys immune system generates antibodies as a defense mechanism against unfamiliar molecules. An anti-antibody is an antibody that binds to other antibodies. Any of a large number of proteins of high molecular weight that are produced normally by specialized B cells after stimulation by an antigen and act specifically against the antigen in an immune response that are produced abnormally by some cancer cells and that typically consist of four subunits including two heavy.
Antibodies are very specific for their intended target. After exposure to a foreign substance called an antigen antibodies continue to circulate in the blood providing protection against future exposures to that antigen. So antibodies directed toward one virus would not protect the body from another.
These antigens are typically other proteins but may be carbohydrates small molecules or even nucleotides. An antibody test is a screening for things called antibodies in your blood.
 Antibody Basics Novus Biologicals
Antibody Basics Novus Biologicals
 Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica
Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica
 What Are Antibodies Definition Function Types Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
What Are Antibodies Definition Function Types Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
 Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica
Antibody Definition Structure Function Types Britannica
 Antibody Basics Novus Biologicals
Antibody Basics Novus Biologicals
 Antibody Structure And Function Sino Biological
Antibody Structure And Function Sino Biological

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.